Java集合框架:Collection接口,Map接口,Collections工具类,Comparable接口,Comparator接口
集合
Java中的集合类是一种工具类,用于存储任意数量的具有共同属性的对象
集合的作用:
- 在类的内部,对数据进行组织
- 简单而快速的搜索大数量的条目
- 有的集合接口,提供了一系列排列有序的元素,并且可以在序列中间快速的插入或者删除有关元素
- 有的集合接口,提供了映射关系,可以通过关键字(key)去快速查找到对应的唯一对象,而这个关键字可以是任意类型
集合和数组的区别:
- 数组的长度固定,集合长度可变
- 数组只能通过下标访问元素,类型固定,而有的集合可以通过任意类型查找所映射的具体对象
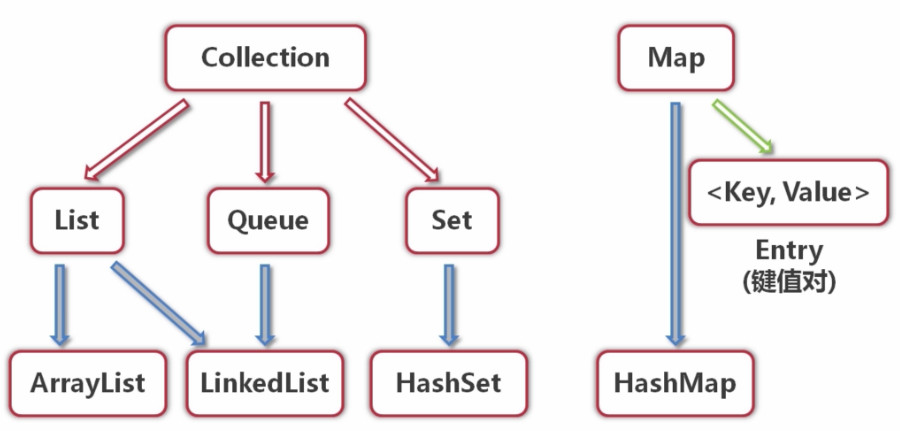
Collection(接口)
- List(接口)(特点:有序,可重复)
- ArrayList(实现类)
- LinkedList(实现类)
- Query(接口)(特点:有序,可重复)
- LinkedList(实现类)
- Set(接口)(特点:无序,不可重复)
- HashSet(实现类)
Map(接口)(特点:Entry(Key,Value) – 键值对:)注:Entry是Map的内部类
- HashSet(实现类)
- HashMap(实现类)
Collection接口是List、Set和Queue接口的父接口,定义了可用于操作List、Set和Queue的方法————增删改查
List
List是元素有序并且可以重复的集合,被称为序列
List可以精确的控制每个元素的插入位置,或删除某个位置元素
ArrayList(数组列表)是List的一个重要实现类,底层是由数组实现的
list.add(对象)把一个对象添加到另一个集合的队尾位置
list.add(index, 对象) 把一个集合添加到另一个集合的指定位置
list.addAll(集合对象) 把一个集合添加到另一个集合的队尾位置
list.addAll(index, 集合对象) 把一个集合添加到另一个集合的指定位置
Arrays.asList(数组) 把一个数组转换成List集合
|
|
集合中的元素可以是任意类型的对象,如果把某个对象放入集合,则会忽略它的类型,而把它当做Object对象处理。泛型则规定了某个集合只可以存放特定类型的对象,会在编译期间进行类型检查
比如上例中的List未规定泛型,则coursesList除了可以添加Course对象外,还可以添加String类型等其他类型,而且在取出其中的元素时,需要进行类型转换
用泛型改进上例
泛型不还可以接受泛型类的子类型
泛型集合中的限定类型不能使用基本数据类型,可以通过包装类使用基本数据类型
Set
Set是元素无序并且不可以重复的集合,被称为集
HashSet(哈希集)是Set的一个重要实现类。
- Set没有像List中set()方法一样就修改,因为List是有序的,可以指定位置,而Set是无序的。
- 查询遍历时,Set不能用get()方法去获取,因为无序没有指定索引ID,但可以使用foreach和iterator来遍历,但是每次遍历出来可能顺序都不一样,还是因为无序造成的。
- Set中的size(),add(),addAll(),remove(),removeAll()与List类似。
- Set还可以添加null,
new HashSet<>().add(null);
|
|
Map
- Map接口提供了一种映射关系,其中的元素是键值对(key-value)的形式存储的,能够实现根据Key快速查找value。Key-value可以是任何对象,是以Entry类型的对象实例存在的。
2.Key是不可以重复的,Value是可以重复的。Key-value都可以为null,不过只能有一个key是null。
3.map支持泛型,Map
4.每个键最多只能映射到一个值
5.Map接口提供了分别返回key值集合(keySet())、value值集合(values())以及Entry(键值对)集合(entrySet() )的方法
HashMap是Map的一个实现类,基于哈希表实现,它根据键的hashCode值存储数据,根据键可以直接获取它的值,具有很快的访问速度。
- Key值和value值都可以为null,但是一个HashMap只能有一个key值为null的映射(key值不可重复)
- HashMap不支持线程的同步,即任一时刻可以有多个线程同时写HashMap,可能会导致数据的不一致。
- 如果需要同步,可以用Collections.synchronizedMap(HashMap map)方法使HashMap具有同步的能力。
- Hashtable与HashMap类似,不同的是:它不允许记录的键或者值为空;
- HashMap中的Entry对象是无序排列的
|
|
contains方法
contains方法用于判断集合中是否包含某个值
不论是List中的 contains 方法,Set中的 contains 方法,以及Map中的 containsKey 和containsValue ,都是遍历寻找第一个匹配的项,因为使用的是equals 方法,所以比较的是对象的引用是否相同,即是否是同一个对象,需要重写类的equals 方法,另外Set的contains 方法和Map中的 containsValue 需要重写 hashCode 方法
Conllections工具类
java.util.Collections工具类是Java集合框架中用来操作集合对象的工具类
排序
根据元素的自然顺序对指定列表按升序进行排序。列表中的所有元素都必须实现 Comparable 接口。
两个接口都可以使用泛型
Comparable接口
定义了默认的比较规则
实现该接口表示:这个类的实例可以比较大小,可以进行自然排序
实现 Comparable 接口必须实现 compareTo 方法,该方法比较此对象与指定对象的顺序。如果该对象小于、等于或大于指定对象,则分别返回负整数、零或正整数。
Comparator接口—–比较工具接口
定义了临时的比较规则
其实现类需要实现 compare()方法,该方法比较用来排序的两个参数。根据第一个参数小于、等于或大于第二个参数分别返回负整数、零或正整数。
|
|